Digit Recognizer
In this project, I did an analysis and some visualizations on the MNSIT dataset.
Published on February 01, 2019 by Udbhav Pangotra
pandas numpy plotly matplotlib
16 min READ
MNIST (“Modified National Institute of Standards and Technology”) is the de facto “hello world” dataset of computer vision. Since its release in 1999, this classic dataset of handwritten images has served as the basis for benchmarking classification algorithms. As new machine learning techniques emerge, MNIST remains a reliable resource for researchers and learners alike.
# MNIST ("Modified National Institute of Standards and Technology") is the de facto “hello world” dataset of computer vision. Since its release in 1999, this classic dataset of handwritten images has served as the basis for benchmarking classification algorithms. As new machine learning techniques emerge, MNIST remains a reliable resource for researchers and learners alike.
# This Python 3 environment comes with many helpful analytics libraries installed
# It is defined by the kaggle/python docker image: https://github.com/kaggle/docker-python
# For example, here's several helpful packages to load in
import numpy as np # linear algebra
import pandas as pd # data processing, CSV file I/O (e.g. pd.read_csv)
# Input data files are available in the "../input/" directory.
# For example, running this (by clicking run or pressing Shift+Enter) will list all files under the input directory
import os
for dirname, _, filenames in os.walk('/kaggle/input'):
for filename in filenames:
print(os.path.join(dirname, filename))
# Any results you write to the current directory are saved as output.
/kaggle/input/digit-recognizer/train.csv
/kaggle/input/digit-recognizer/sample_submission.csv
/kaggle/input/digit-recognizer/test.csv
train = pd.read_csv('/kaggle/input/digit-recognizer/train.csv')
test = pd.read_csv('/kaggle/input/digit-recognizer/test.csv')
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.image as mpimg
import seaborn as sns
%matplotlib inline
np.random.seed(2)
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
import itertools
from keras.utils.np_utils import to_categorical # convert to one-hot-encoding
from keras.models import Sequential
from keras.layers import Dense, Dropout, Flatten, Conv2D, MaxPool2D
from keras.optimizers import RMSprop
from keras.preprocessing.image import ImageDataGenerator
from keras.callbacks import ReduceLROnPlateau
sns.set(style='white', context='notebook', palette='deep')
Using TensorFlow backend.
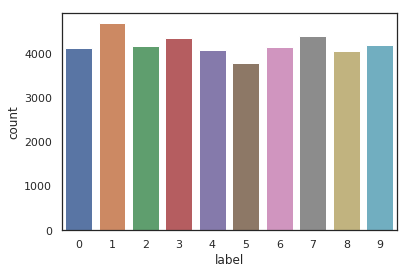
Y_train = train["label"]
X_train = train.drop(labels = ["label"],axis = 1)
g = sns.countplot(Y_train)
Y_train.value_counts()
1 4684
7 4401
3 4351
9 4188
2 4177
6 4137
0 4132
4 4072
8 4063
5 3795
Name: label, dtype: int64
X_train.isna().any().sum(),test.isna().any().sum()
(0, 0)
X_train=X_train/255
test=test/255
# Reshape image in 3 dimensions (height = 28px, width = 28px , canal = 1)
X_train = X_train.values.reshape(-1,28,28,1)
test = test.values.reshape(-1,28,28,1)
Y_train = to_categorical(Y_train, num_classes = 10)
random_seed = 2
X_train, X_val, Y_train, Y_val = train_test_split(X_train, Y_train, test_size = 0.1, random_state=random_seed)
X_train.shape
(37800, 28, 28, 1)
g = plt.imshow(X_train[0][:,:,0])
# Set the CNN model
# my CNN architechture is In -> [[Conv2D->relu]*2 -> MaxPool2D -> Dropout]*2 -> Flatten -> Dense -> Dropout -> Out
model = Sequential()
model.add(Conv2D(filters = 32, kernel_size = (5,5),padding = 'Same',
activation ='relu', input_shape = (28,28,1)))
model.add(Conv2D(filters = 32, kernel_size = (5,5),padding = 'Same',
activation ='relu'))
model.add(MaxPool2D(pool_size=(2,2)))
model.add(Dropout(0.25))
model.add(Conv2D(filters = 64, kernel_size = (3,3),padding = 'Same',
activation ='relu'))
model.add(Conv2D(filters = 64, kernel_size = (3,3),padding = 'Same',
activation ='relu'))
model.add(MaxPool2D(pool_size=(2,2), strides=(2,2)))
model.add(Dropout(0.25))
model.add(Flatten())
model.add(Dense(256, activation = "relu"))
model.add(Dropout(0.5))
model.add(Dense(10, activation = "softmax"))
optimizer = RMSprop(lr=0.001, rho=0.9, epsilon=1e-08, decay=0.0)
model.compile(optimizer = optimizer , loss = "categorical_crossentropy", metrics=["accuracy"])
# Set a learning rate annealer
learning_rate_reduction = ReduceLROnPlateau(monitor='val_accuracy',
patience=3,
verbose=1,
factor=0.5,
min_lr=0.00001)
epochs = 50 #
batch_size = 86
datagen = ImageDataGenerator(
featurewise_center=False, # set input mean to 0 over the dataset
samplewise_center=False, # set each sample mean to 0
featurewise_std_normalization=False, # divide inputs by std of the dataset
samplewise_std_normalization=False, # divide each input by its std
zca_whitening=False, # apply ZCA whitening
rotation_range=10, # randomly rotate images in the range (degrees, 0 to 180)
zoom_range = 0.1, # Randomly zoom image
width_shift_range=0.1, # randomly shift images horizontally (fraction of total width)
height_shift_range=0.1, # randomly shift images vertically (fraction of total height)
horizontal_flip=False, # randomly flip images
vertical_flip=False) # randomly flip images
datagen.fit(X_train)
# Fit the model
history = model.fit_generator(datagen.flow(X_train,Y_train, batch_size=batch_size),
epochs = epochs, validation_data = (X_val,Y_val),
verbose = 2, steps_per_epoch=X_train.shape[0] // batch_size
, callbacks=[learning_rate_reduction])
Epoch 1/50
- 253s - loss: 0.4054 - accuracy: 0.8698 - val_loss: 0.0646 - val_accuracy: 0.9812
Epoch 2/50
- 249s - loss: 0.1321 - accuracy: 0.9603 - val_loss: 0.0505 - val_accuracy: 0.9857
Epoch 3/50
- 249s - loss: 0.0963 - accuracy: 0.9719 - val_loss: 0.0467 - val_accuracy: 0.9864
Epoch 4/50
- 247s - loss: 0.0813 - accuracy: 0.9760 - val_loss: 0.0359 - val_accuracy: 0.9900
Epoch 5/50
- 254s - loss: 0.0736 - accuracy: 0.9788 - val_loss: 0.0248 - val_accuracy: 0.9924
Epoch 6/50
- 257s - loss: 0.0663 - accuracy: 0.9809 - val_loss: 0.0226 - val_accuracy: 0.9919
Epoch 7/50
- 247s - loss: 0.0636 - accuracy: 0.9813 - val_loss: 0.0403 - val_accuracy: 0.9874
Epoch 8/50
- 246s - loss: 0.0615 - accuracy: 0.9820 - val_loss: 0.0200 - val_accuracy: 0.9933
Epoch 9/50
- 248s - loss: 0.0605 - accuracy: 0.9822 - val_loss: 0.0356 - val_accuracy: 0.9905
Epoch 10/50
- 250s - loss: 0.0605 - accuracy: 0.9831 - val_loss: 0.0239 - val_accuracy: 0.9929
Epoch 11/50
- 248s - loss: 0.0592 - accuracy: 0.9832 - val_loss: 0.0278 - val_accuracy: 0.9921
Epoch 00011: ReduceLROnPlateau reducing learning rate to 0.0005000000237487257.
Epoch 12/50
- 254s - loss: 0.0435 - accuracy: 0.9871 - val_loss: 0.0235 - val_accuracy: 0.9924
Epoch 13/50
- 250s - loss: 0.0438 - accuracy: 0.9877 - val_loss: 0.0197 - val_accuracy: 0.9943
Epoch 14/50
- 258s - loss: 0.0433 - accuracy: 0.9872 - val_loss: 0.0215 - val_accuracy: 0.9940
Epoch 15/50
- 285s - loss: 0.0404 - accuracy: 0.9887 - val_loss: 0.0243 - val_accuracy: 0.9948
Epoch 16/50
- 282s - loss: 0.0459 - accuracy: 0.9873 - val_loss: 0.0242 - val_accuracy: 0.9943
Epoch 17/50
- 279s - loss: 0.0439 - accuracy: 0.9876 - val_loss: 0.0242 - val_accuracy: 0.9938
Epoch 18/50
- 279s - loss: 0.0424 - accuracy: 0.9877 - val_loss: 0.0296 - val_accuracy: 0.9931
Epoch 00018: ReduceLROnPlateau reducing learning rate to 0.0002500000118743628.
Epoch 19/50
- 283s - loss: 0.0364 - accuracy: 0.9896 - val_loss: 0.0246 - val_accuracy: 0.9938
Epoch 20/50
- 284s - loss: 0.0352 - accuracy: 0.9895 - val_loss: 0.0161 - val_accuracy: 0.9950
Epoch 21/50
- 282s - loss: 0.0355 - accuracy: 0.9903 - val_loss: 0.0260 - val_accuracy: 0.9936
Epoch 22/50
- 281s - loss: 0.0355 - accuracy: 0.9900 - val_loss: 0.0275 - val_accuracy: 0.9933
Epoch 23/50
- 278s - loss: 0.0361 - accuracy: 0.9903 - val_loss: 0.0181 - val_accuracy: 0.9948
Epoch 00023: ReduceLROnPlateau reducing learning rate to 0.0001250000059371814.
Epoch 24/50
- 281s - loss: 0.0339 - accuracy: 0.9909 - val_loss: 0.0215 - val_accuracy: 0.9945
Epoch 25/50
- 287s - loss: 0.0354 - accuracy: 0.9904 - val_loss: 0.0260 - val_accuracy: 0.9940
Epoch 26/50
- 283s - loss: 0.0325 - accuracy: 0.9906 - val_loss: 0.0204 - val_accuracy: 0.9945
Epoch 00026: ReduceLROnPlateau reducing learning rate to 6.25000029685907e-05.
Epoch 27/50
- 283s - loss: 0.0297 - accuracy: 0.9912 - val_loss: 0.0219 - val_accuracy: 0.9938
Epoch 28/50
- 282s - loss: 0.0287 - accuracy: 0.9917 - val_loss: 0.0229 - val_accuracy: 0.9936
Epoch 29/50
- 280s - loss: 0.0272 - accuracy: 0.9921 - val_loss: 0.0225 - val_accuracy: 0.9938
Epoch 00029: ReduceLROnPlateau reducing learning rate to 3.125000148429535e-05.
Epoch 30/50
- 280s - loss: 0.0276 - accuracy: 0.9919 - val_loss: 0.0223 - val_accuracy: 0.9945
Epoch 31/50
- 281s - loss: 0.0281 - accuracy: 0.9914 - val_loss: 0.0210 - val_accuracy: 0.9943
Epoch 32/50
- 284s - loss: 0.0277 - accuracy: 0.9923 - val_loss: 0.0209 - val_accuracy: 0.9945
Epoch 00032: ReduceLROnPlateau reducing learning rate to 1.5625000742147677e-05.
Epoch 33/50
- 282s - loss: 0.0263 - accuracy: 0.9923 - val_loss: 0.0222 - val_accuracy: 0.9943
Epoch 34/50
- 279s - loss: 0.0276 - accuracy: 0.9918 - val_loss: 0.0212 - val_accuracy: 0.9943
Epoch 35/50
- 279s - loss: 0.0265 - accuracy: 0.9930 - val_loss: 0.0218 - val_accuracy: 0.9943
Epoch 00035: ReduceLROnPlateau reducing learning rate to 1e-05.
Epoch 36/50
- 281s - loss: 0.0287 - accuracy: 0.9921 - val_loss: 0.0212 - val_accuracy: 0.9948
Epoch 37/50
- 280s - loss: 0.0281 - accuracy: 0.9918 - val_loss: 0.0209 - val_accuracy: 0.9945
Epoch 38/50
- 288s - loss: 0.0282 - accuracy: 0.9919 - val_loss: 0.0206 - val_accuracy: 0.9945
Epoch 39/50
- 282s - loss: 0.0271 - accuracy: 0.9924 - val_loss: 0.0217 - val_accuracy: 0.9945
Epoch 40/50
- 283s - loss: 0.0257 - accuracy: 0.9929 - val_loss: 0.0220 - val_accuracy: 0.9943
Epoch 41/50
- 284s - loss: 0.0280 - accuracy: 0.9918 - val_loss: 0.0222 - val_accuracy: 0.9943
Epoch 42/50
- 285s - loss: 0.0284 - accuracy: 0.9920 - val_loss: 0.0209 - val_accuracy: 0.9948
Epoch 43/50
- 282s - loss: 0.0262 - accuracy: 0.9928 - val_loss: 0.0212 - val_accuracy: 0.9945
Epoch 44/50
- 285s - loss: 0.0266 - accuracy: 0.9926 - val_loss: 0.0207 - val_accuracy: 0.9948
Epoch 45/50
- 286s - loss: 0.0279 - accuracy: 0.9916 - val_loss: 0.0203 - val_accuracy: 0.9945
Epoch 46/50
- 283s - loss: 0.0257 - accuracy: 0.9926 - val_loss: 0.0206 - val_accuracy: 0.9945
Epoch 47/50
- 283s - loss: 0.0286 - accuracy: 0.9915 - val_loss: 0.0212 - val_accuracy: 0.9945
Epoch 48/50
- 282s - loss: 0.0270 - accuracy: 0.9925 - val_loss: 0.0211 - val_accuracy: 0.9945
Epoch 49/50
- 282s - loss: 0.0275 - accuracy: 0.9918 - val_loss: 0.0206 - val_accuracy: 0.9945
Epoch 50/50
- 283s - loss: 0.0273 - accuracy: 0.9921 - val_loss: 0.0210 - val_accuracy: 0.9945
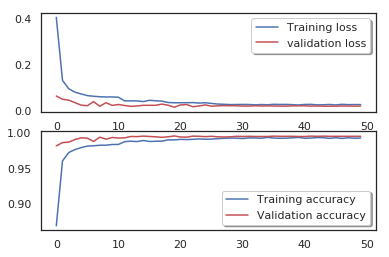
fig, ax = plt.subplots(2,1)
ax[0].plot(history.history['loss'], color='b', label="Training loss")
ax[0].plot(history.history['val_loss'], color='r', label="validation loss",axes =ax[0])
legend = ax[0].legend(loc='best', shadow=True)
ax[1].plot(history.history['accuracy'], color='b', label="Training accuracy")
ax[1].plot(history.history['val_accuracy'], color='r',label="Validation accuracy")
legend = ax[1].legend(loc='best', shadow=True)
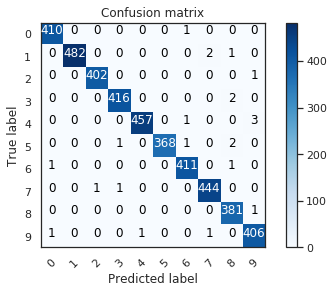
# Look at confusion matrix
def plot_confusion_matrix(cm, classes,
normalize=False,
title='Confusion matrix',
cmap=plt.cm.Blues):
"""
This function prints and plots the confusion matrix.
Normalization can be applied by setting `normalize=True`.
"""
plt.imshow(cm, interpolation='nearest', cmap=cmap)
plt.title(title)
plt.colorbar()
tick_marks = np.arange(len(classes))
plt.xticks(tick_marks, classes, rotation=45)
plt.yticks(tick_marks, classes)
if normalize:
cm = cm.astype('float') / cm.sum(axis=1)[:, np.newaxis]
thresh = cm.max() / 2.
for i, j in itertools.product(range(cm.shape[0]), range(cm.shape[1])):
plt.text(j, i, cm[i, j],
horizontalalignment="center",
color="white" if cm[i, j] > thresh else "black")
plt.tight_layout()
plt.ylabel('True label')
plt.xlabel('Predicted label')
# Predict the values from the validation dataset
Y_pred = model.predict(X_val)
# Convert predictions classes to one hot vectors
Y_pred_classes = np.argmax(Y_pred,axis = 1)
# Convert validation observations to one hot vectors
Y_true = np.argmax(Y_val,axis = 1)
# compute the confusion matrix
confusion_mtx = confusion_matrix(Y_true, Y_pred_classes)
# plot the confusion matrix
plot_confusion_matrix(confusion_mtx, classes = range(10))
# predict results
results = model.predict(test)
# select the indix with the maximum probability
results = np.argmax(results,axis = 1)
results = pd.Series(results,name="Label")
submission = pd.concat([pd.Series(range(1,28001),name = "ImageId"),results],axis = 1)
submission.to_csv("cnn_mnist_datagen.csv",index=False)